In Linux, managing processes is a key part of system administration. You can identify and terminate (or “kill”) processes using several commands. Here’s a guide on how to identify and kill a running process on a Linux server.
1. Identify a Process by Name or ID #
The first step is to identify the process you want to stop. This can be done using commands like ps, top, htop, and pgrep.
Using ps Command #
The ps command shows a snapshot of current processes.
- List all processes:
- Note the PID of the process that you want to kill
ps aux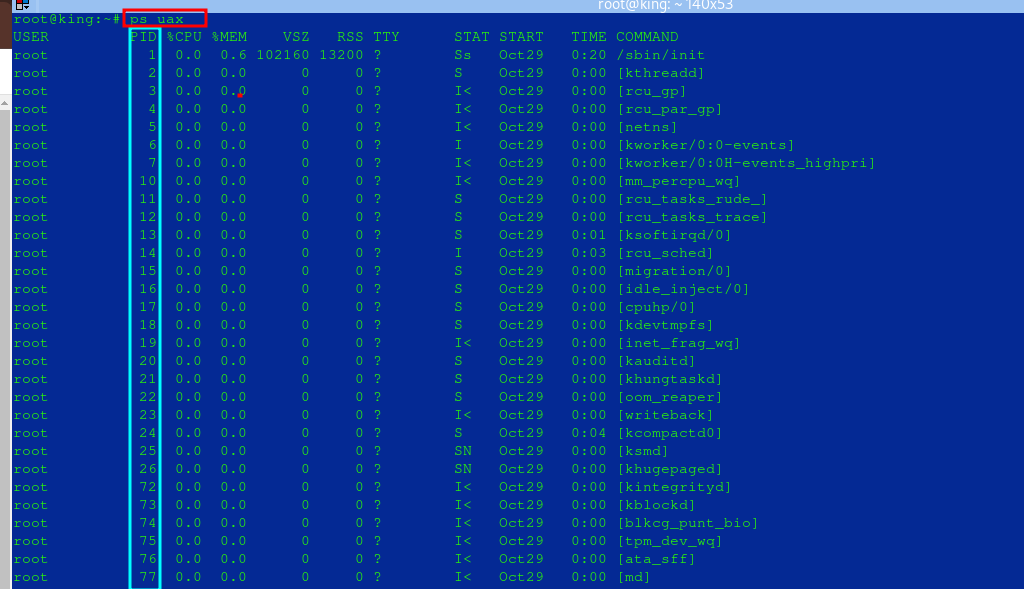
- Find a specific process by name:
- Replace
process_namewith the name of the process you’re searching for. - Take note of the PID
- Replace
ps aux | grep process_name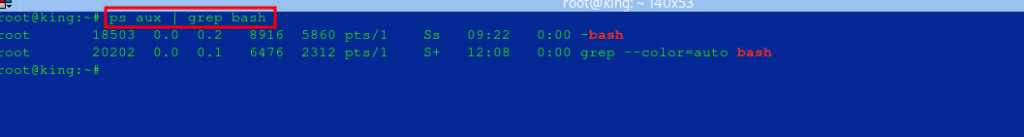
Using top Command #
top provides a real-time view of running processes and can help you identify high-resource-consuming processes.
- Start
top:- Note the PID of the process you want to kill.
- Press
qto quittop.
top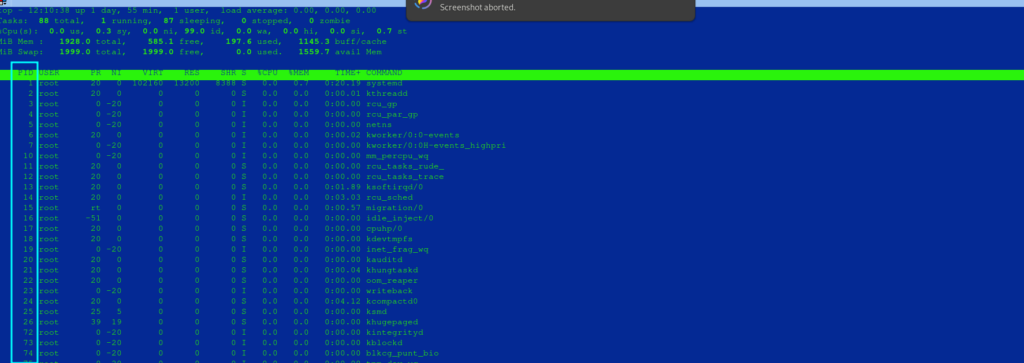
Using htop (if installed) #
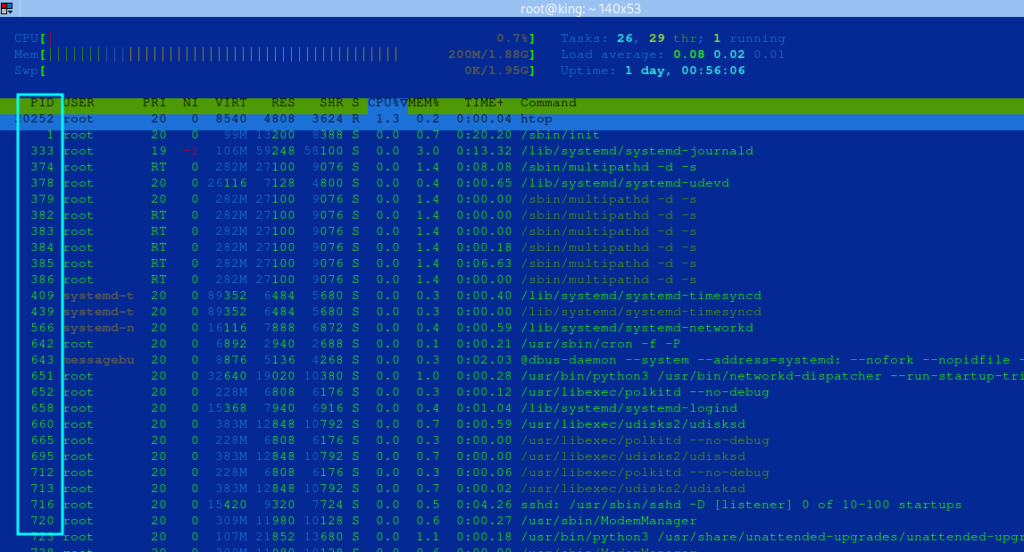
htop is an interactive tool that provides an easy-to-use interface for managing processes.
- Start
htop:
htop- Navigate to the process and press
F9to kill it.
2. Kill a Process by PID #
Once you’ve identified the PID of the process, you can use the kill command to terminate it.
- Basic kill command:
- Replace
PIDwith the actual process ID.
- Replace
kill PID
- Common Kill Signals
The kill command uses different signals to terminate a process:
- SIGTERM (signal 15): Politely asks a process to stop.
- If you input a PID that does not exist, you will see an output that says there is no such process.
kill -15 PID
SIGKILL (signal 9): Forces a process to stop immediately, without cleanup.
kill -9 PID3. Kill All Instances of a Process by Name #
To kill all instances of a particular process by name, use the pkill or killall commands.
Using pkill #
pkill can terminate processes based on their name.
- Kill processes by name:
pkill process_name
Using killall #
killall kills all instances of a process by name. This is useful for stopping multiple instances.
- Kill all instances of a process:
killall process_name
4. Check if the Process was Successfully Terminated #
Use either of the commands below to check if the process is still running.
ps aux | grep process_name or pgrep process_name

Summary of Commands #
- Identify Process:
ps auxpgrep process_nametoporhtop
- Kill Process by PID:
kill PIDkill -9 PID(force kill)
- Kill All by Name:
pkill process_namekillall process_name
These commands provide an efficient way to identify and kill processes on Linux, essential for effective system management and troubleshooting.